Have you ever seen wisps of smoke drifting from smokestacks and wondered how much of that energy they are releasing in the air without utilizing it? Maybe a lot less than you think since saving energy is a very big problem and can be pretty costly for a lot of factories or businesses and that is why they install heat exchangers to salvage as much heat as they can from waste gases. Heat exchangers have a big role in our daily lives too. Engines in planes, cars, and ships also use heat exchangers to work more efficiently, and if you have an air-conditioner or refrigerator at home, those devices are using heat exchangers too. So what are heat exchangers and how do they exactly work?
What is a heat exchanger?
You probably have or had at one point a central heating furnace (or a boiler) at home that heated your radiators with hot-water in the various rooms of your home. These devices work by burning some type of natural gas and then hot gas jets fire in a line over water that is circulating through the network of pipes inside your walls. As the water flows throughout the pipes, it absorbs the heat energy from them and heats up. This is exactly what the term heat exchangers means. While the gas jets cold down, the water heats up. The most common use for heat exchangers is in vehicles.

A heat exchanger is a device that allows heat to transfer from one fluid to pass to a second fluid without the two fluids ever coming in any kind of direct contact.
If you want to know more about the uses for water heat exchangers, check out www.exodraft-varmeatervinning.se
What are heat exchangers used for?
You can see heat exchangers used in all kinds of places, usually used to cool or heat buildings or even help engines or similar machines to work more efficiently. Air-conditioners and refrigerators work completely the opposite way of central heating systems. They remove the heat from a room (or refrigerator compartment) and then the heat transfers to a fluid that dissipates the heat out of the way. In power plants or other factories, exhaust gases can contain massive amounts of heat that are usually released into the open air.
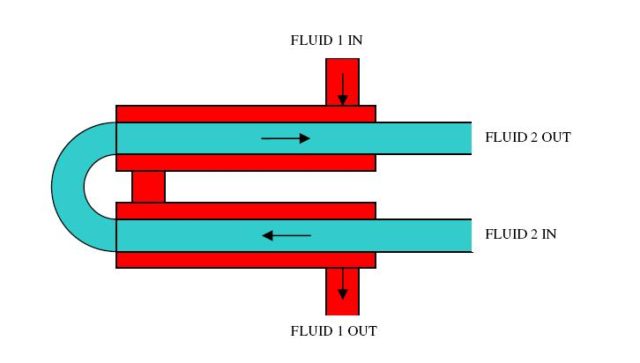
This release of hot air, if not utilized, can be a great loss of energy for the factories. The way to solve this problem properly is with heat exchangers that should be placed inside smokestacks. As the hot exhaust gasses are released up in the air, they move past the copper pipes that have water flowing in them. The water then carries the heat away from where it can be reused, by warming the cold gases that constantly feed into the furnaces, saving the energy that would be used to heat them. The excess heat can also be used to heat up employees’ headquarters or offices.
There are hundreds of other uses for heat exchangers that we simply cannot list them all in just one article and even more impossible to explain them.